Biochemistry laboratory instruments are specialized tools used to perform a wide range of experiments and analyses in the field of biochemistry. These instruments are designed to measure, manipulate, and analyze biological samples, enabling researchers to understand the chemical processes occurring within living organisms.
2. Spectrophotometer
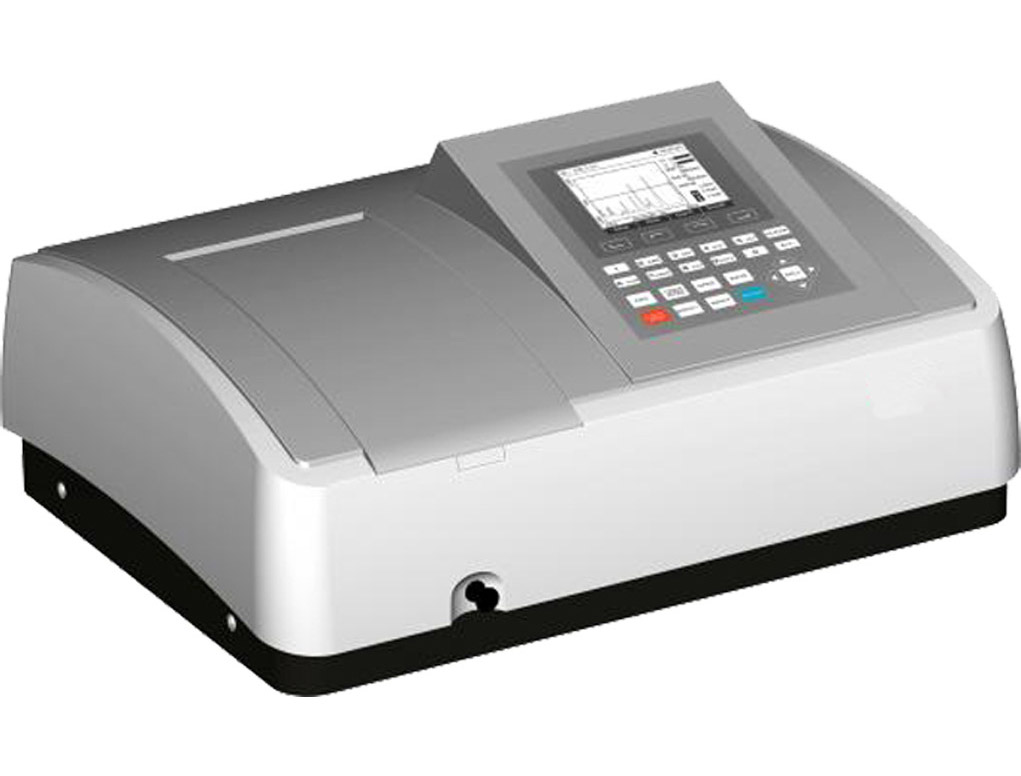
A spectrophotometer is a fundamental instrument used in biochemistry labs to measure the absorption or transmission of light by a sample. It is widely utilized in quantifying the concentration of biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, based on their light-absorbing properties. Spectrophotometers are invaluable tools for determining enzyme kinetics, conducting DNA quantification assays, and analyzing the purity of biomolecules.

3. Centrifuge
A centrifuge is a vital instrument in biochemistry labs that separates mixtures based on their density gradients. By spinning samples at high speeds, a centrifuge allows the separation of different components, such as cells, organelles, or subcellular particles. This instrument enables researchers to isolate specific biomolecules or perform cell fractionation, leading to a better understanding of cellular processes and molecular interactions.

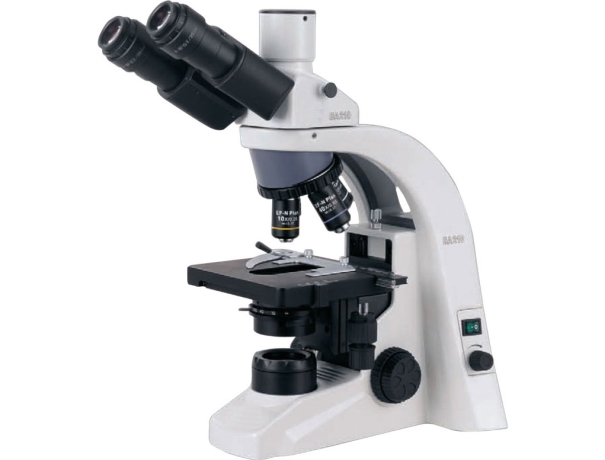
4. Microscope
Microscopes are indispensable tools in biochemistry labs, providing researchers with the ability to visualize and analyze biological samples at the cellular and molecular levels. These instruments enable the observation of cellular structures, organelles, and molecular interactions, aiding in the study of cell biology, histology, and molecular genetics. Various types of microscopes, including light microscopes, fluorescence microscopes, and electron microscopes, offer different levels of resolution and imaging capabilities.
5. pH Meter
pH meters are essential instruments used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. In biochemistry labs, pH meters play a crucial role in maintaining optimal conditions for enzymatic reactions, cell cultures, and buffer preparations. Accurate pH measurements are vital for studying enzymatic activities, optimizing reaction conditions, and ensuring the stability of biological samples.
6. Analytical Balance
An analytical balance is a precise weighing instrument used in biochemistry labs to measure the mass of samples and reagents with high accuracy. It is crucial for preparing precise solutions, determining the concentrations of compounds, and weighing small quantities of biomolecules. The analytical balance ensures reproducibility and accuracy in biochemical experiments, contributing to the reliability of research outcomes.
7. Incubator
Incubators are temperature-controlled chambers used in biochemistry labs to provide an optimal environment for the growth and maintenance of cell cultures, microorganisms, and enzymatic reactions.
8. Autoclave
Autoclaves are high-pressure steam sterilization devices used to eliminate microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, from laboratory equipment and glassware. In biochemistry labs, maintaining sterile conditions is crucial to prevent contamination and ensure the accuracy and reliability of experimental results. Autoclaves effectively sterilize laboratory instruments, media, and other materials, promoting aseptic techniques and safe experimental practices.
9. Gel Electrophoresis System
Gel electrophoresis systems are utilized to separate and analyze biomolecules, primarily nucleic acids and proteins, based on their size, charge, and molecular weight. These systems employ an electric field to move charged molecules through a gel matrix, resulting in distinct bands that can be visualized and analyzed. Gel electrophoresis is a fundamental technique in biochemistry labs for DNA sequencing, genotyping, protein analysis, and the identification of genetic variations.
10. PCR Machine
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) machine is a cornerstone instrument in biochemistry labs, enabling the amplification of specific DNA sequences. PCR is a powerful technique used in various applications, including gene cloning, DNA sequencing, and gene expression analysis. PCR machines provide precise temperature control for the denaturation, annealing, and extension steps involved in the amplification process, facilitating the study of genes and genetic variations.
11. HPLC System
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) systems are sophisticated instruments used for the separation, identification, and quantification of chemical compounds in complex mixtures. In biochemistry labs, HPLC plays a vital role in analyzing biomolecules, such as amino acids, peptides, nucleotides, and metabolites. HPLC systems offer high resolution, sensitivity, and specificity, contributing to the characterization of biological samples and the elucidation of biochemical pathways.
12. NMR Spectrometer
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectrometers are powerful instruments that provide detailed structural and chemical information about molecules. In biochemistry labs, NMR spectroscopy is used to determine the three-dimensional structures of proteins and study their interactions with ligands, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules. NMR spectrometers utilize the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei, offering valuable insights into molecular dynamics, conformational changes, and protein folding.
13. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) systems combine two analytical techniques to separate and identify chemical compounds in complex mixtures. GC separates compounds based on their volatility, while MS identifies and quantifies the separated compounds based on their mass-to-charge ratio. In biochemistry labs, GC-MS is used for analyzing volatile metabolites, identifying drug metabolites, and studying metabolic pathways in organisms.