BIOLOGICAL MICROSCOPES By MRC.For personal advice leave details
Primary Manufacturer:
Motic
Motic is a huge manufacturer of MICROSCOPES and MICROSCOPES accessories.
Motic -since 1988.
Motic is one of the first microscope manufacturers who started to develop digital microscopy solutions, digital imaging products and application software
How biological microscopes work
Biological microscopes take transparent samples.optical microscope that is primarily designed to observe cells, tissues, and other biological specimens. These specimens correspond to flora and fauna specimens and any translucent or predominantly light industrial specimen. The method of sampling in the biological microscope is carried out by sampling between the light source and the field lenses in such a way that light passes through it and reaches the lenses.A biological microscope allows viewing of: different cells and their contents, different tissue sections, smallest plant structures, small creatures such as: amoebae, cells, bacteria, biological samples and more.biology microscopes are ideal for clinical, University and Institutional applications
Biological microscopes are specialized optical instruments used to observe the structure and function of living organisms, cells, and tissue samples. Biological microscopes enable researchers to identify different samples' structures, differentiate between normal and abnormal cells, analyze cell behavior in response to changes such as temperature or chemical reactions, and monitor interactions between separate components.
We usually observe microscopic samples of specimens through a biological or compound microscope. But, the biological microscope is not only limited to viewing cells and tissue samples; it is also used in other fields such as biochemistry, microbiology, and even astronomy.
Stereo Microscopes or Dissecting Microscopes can create three-dimensional images of specimens and objects too large to be seen with the naked eye. Digital Microscopes are a modern innovation used to capture high-resolution images and videos of a specimen from different angles.
The compound microscope is the most commonly used type of biological microscope, which uses lenses to enlarge images of specimens. The lenses can magnify objects up to 1000 times their actual size allowing researchers to see minute details that would otherwise be impossible to observe with the human eye.
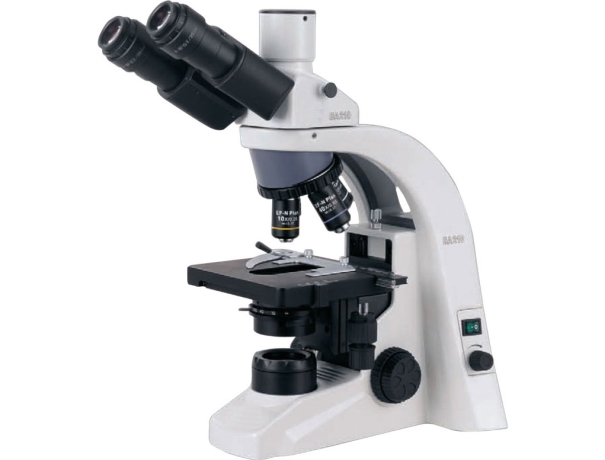
What To See With Biological Microscopes?
Biological microscopes can be used to observe and study a variety of specimens, from cells and tissues to bacteria and viruses. They allow researchers to identify different structures within a sample and monitor the behavior of these structures in response to various changes such as temperature or chemical reactions. In addition, biological microscopes can also be used to identify abnormal cells or analyze the effects of drugs on living organisms.
Furthermore, biological microscopes are often used in forensic science for identification purposes. By viewing specimens closely with a microscope, scientists can compare different characteristics between samples which helps them determine if two samples came from the same source.
Biological Microscope Working Process
Biological microscopes use light passing through a series of lenses to magnify the image of a specimen. The first lens, called an objective lens, collects the light rays and focuses them on a small specimen area, creating an enlarged version. Trans-illumination light method is used to make the specimen more visible. The light is directed onto the sample from below, and a filter is used to reduce glare, allowing researchers to see even the smallest details within a sample.
The second lens, usually called an ocular lens, projects the image further onto an eyepiece, making it possible for researchers to view the magnified image of a specimen. Finally, you can achieve additional magnifications with auxiliary lenses.
Most biological microscopes have three to five lenses that provide magnifications between 4x and 100x. You can select each lens by rotating the turret to the lens of your choice.
Biological microscopes are used in medicine, school laboratories, biology, and biochemistry laboratories to observe living specimens, diagnose diseases, identify cells and tissues and monitor their behavior. Students also use them to learn more about the structure of plants and animals and their interactions.
By using a biological microscope, researchers can gain valuable insights into the intricate workings of different samples, which will help them make informed decisions regarding research and development.