It is expressed in milligrams per liter (mg/L) also referred to as ppm (parts per million), which indicates the mass of oxygen consumed per liter of solution.
Test Chemical Oxygen Demand
The Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) test uses a strong chemical oxidant in an acid solution and heat to oxidize organic carbon to CO2 and H2O.
Oxygen demand is determined by measuring the amount of oxidant consumed using titrimetric or photometric methods.
The test is not adversely affected by toxic substances, and test data is available in 1-1/2 to 3 hours, providing faster water quality assessment and process control.
Typical DIgestion Curves - COD vs. Time:
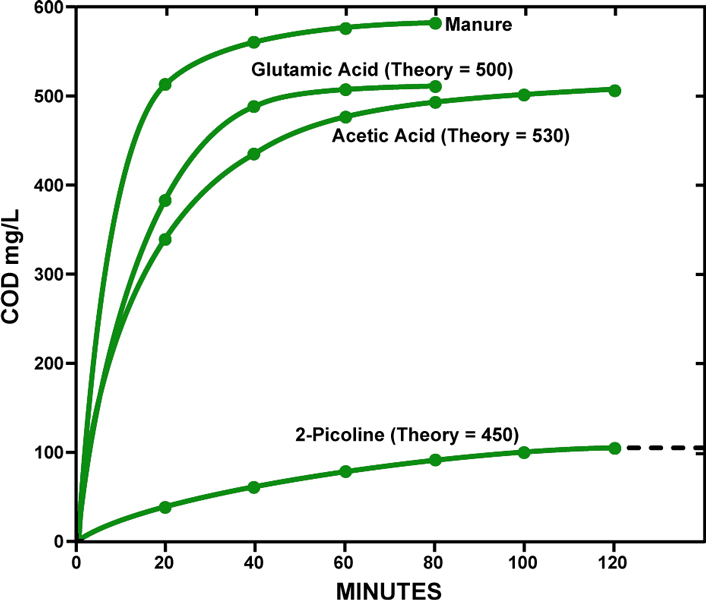
COD determinations made for process control purposes can be conducted in a shorter digestion time than specified in the procedure. For samples that are difficult to oxidize, the digestion time can be extended up to four hours if a blank is also run for the same period of time.


What are the Chemical oxygen demand
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is a measure of the amount of oxygen required to oxidize organic matter in water. It is commonly used as a measure of water quality and is an important parameter in the treatment of wastewater. The COD test is used to determine the concentration of organic compounds in a water sample, which can be an indicator of the level of contamination.
A laboratory COD reactor is a device used to perform the COD test in a controlled laboratory environment. It consists of a container with a volume of known volume, typically around 500 mL, and a heating element to bring the water sample to a specified temperature. The reactor also includes a source of oxygen, such as an oxygen gas cylinder, and a means of stirring the water sample to ensure thorough mixing.
How to perform the test
To perform the COD test, a known volume of water sample is placed in the COD reactor and the temperature is raised to a specified temperature, typically around 150°C. The oxygen source is then opened and the water sample is stirred to ensure that the oxygen is well-mixed with the sample. The COD reactor is then sealed and the reaction is allowed to proceed for a specific period of time, typically around two hours.
After the specified reaction time, the COD reactor is cooled and the concentration of oxygen in the water sample is measured. The COD is calculated by comparing the initial concentration of oxygen in the water sample to the final concentration, after the reaction has occurred. The COD is expressed in milligrams of oxygen per liter of water sample (mg/L).
The COD test is an important tool for determining the level of organic contamination in water and is used in a variety of applications, including monitoring the quality of drinking water, evaluating the effectiveness of wastewater treatment systems, and assessing the environmental impact of industrial discharges. Laboratory COD reactors are an essential part of these efforts, providing a controlled environment for accurately performing the COD test and obtaining reliable results.
For more information