Laboratory Freeze Dryers / laboratory lyophilizers
Freeze-drying For lab, also known as lyophilisation, lyophilization, or cryodesiccation, is a dehydration process typically used to preserve a perishable material or make the material more convenient for transport. Freeze-drying works by freezing the material and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water in the material to sublimate directly from the solid phase to the gas phase.

Here are four stages in the complete drying process: pretreatment, freezing, primary drying, and secondary drying.
Applications of Freeze-Drying-Lyophilisation
- Food industry-Freeze-drying is used to preserve food, the resulting product being very lightweight.
- Technological industry-In chemical synthesis, products are often freeze-dried to make them more stable, or easier to dissolve in water for subsequent use.
- Document Conservation-freeze-drying can use as a recovery method of water-damaged books and documents.
- In bacteriology freeze-drying is used to conserve special strains.
- Advanced ceramics processes sometimes use freeze-drying to create a formable powder from a sprayed slurry mist
- Floral preservation-Wedding bouquet preservation
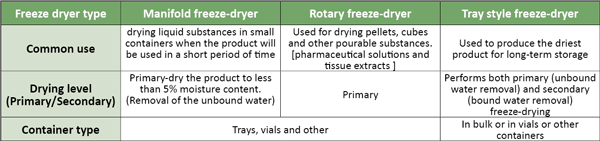
Types of Laboratory Freeze-dryers:
How does the Laboratory Freeze dryer works?
Laboratory Freeze-dryers first freezes the material, then the device reduces pressure and adds while heat to allow the movement of water. There are actually 3 main actions: Freezing, Sublimation , Adsorption
