A microbiology laboratory is a specialized scientific facility that is focused on the study of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Microbiology laboratories are typically found in hospitals, research institutions, and universities, and are often used for a wide range of research and diagnostic purposes.
Microbiology laboratories are equipped with a range of specialized equipment and tools that are used to identify, cultivate, and study microorganisms. This may include microscopes, incubators, centrifuges, and a variety of other laboratory instruments and supplies. Microbiology laboratories may also have specialized facilities, such as clean rooms and biosafety cabinets, that are used to handle and manipulate potentially hazardous microorganisms in a safe and controlled manner.
Types of work in a microbiology laboratory
The types of work that are carried out in microbiology laboratories can vary widely, depending on the specific focus of the laboratory and the needs of the researchers or clinicians who are using the facility. Some common types of work that may be carried out in a microbiology laboratory include:
Identifying and characterizing microorganisms: This may involve using various techniques, such as microscopy, culture-based methods, and molecular methods, to identify and classify microorganisms based on their characteristics and properties.
Cultivating and propagating microorganisms: This may involve growing microorganisms in the laboratory under controlled conditions in order to study their growth and behavior, or to produce large quantities of microorganisms for use in other research or diagnostic applications.
Studying the genetics and metabolism of microorganisms: This may involve using techniques such as DNA sequencing and metabolic profiling to investigate the genetic makeup and metabolic pathways of microorganisms.
Developing and testing new diagnostic tests: This may involve developing and evaluating new methods for detecting and identifying microorganisms, or for determining the presence or absence of specific microorganisms in clinical samples.
Conducting research on the role of microorganisms in various diseases: This may involve studying the interactions between microorganisms and host organisms, or investigating the role of microorganisms in the development and progression of various diseases.
One example of research that may be conducted in a microbiology laboratory is studying the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. This research may involve identifying the genes that allow bacteria to become resistant to antibiotics, as well as developing new strategies for combating antibiotic resistance.
To conduct this research, scientists may use a variety of techniques, including genetic engineering, microscopy, and biochemical assays. They may also use computer simulations and other computational tools to analyze data and build models of bacterial behavior.
Microbiology laboratories typically provide a wide range of services to researchers, clinicians, and other clients. These may include diagnostic testing and identification services, consulting and advisory services, and research and development services. Some microbiology laboratories may also offer training and education programs for professionals who are interested in pursuing careers in the field of microbiology.

What research is carried out in microbiology laboratories?
Microbiology laboratories are used for a wide range of research purposes, and the specific types of research that are carried out in these facilities can vary widely depending on the focus and mission of the laboratory and the needs of the researchers who are using the facility. Some common types of research that may be conducted in microbiology laboratories include:
Basic research on the biology and genetics of microorganisms: This type of research may involve studying the structure, function, and genetics of microorganisms in order to better understand their role in various ecological and biological systems. This type of research may also involve investigating the evolution and diversity of microorganisms, as well as the mechanisms that govern their growth and behavior.
Research on the role of microorganisms in human health and disease: This type of research may involve studying the interactions between microorganisms and host organisms, and investigating the role of microorganisms in the development and progression of various diseases. This type of research may also involve developing and testing new diagnostic tests and treatments for infectious diseases.
Environmental microbiology research: This type of research may involve studying the role of microorganisms in various ecological systems, including aquatic, terrestrial, and atmospheric environments. This type of research may also involve investigating the mechanisms by which microorganisms influence various environmental processes, such as nutrient cycling and decomposition.
Agricultural and food microbiology research: This type of research may involve studying the role of microorganisms in various agricultural and food production processes, including the fermentation of food and the development of food-borne illnesses. This type of research may also involve developing and testing new methods for improving food safety and quality.
Industrial microbiology research: This type of research may involve studying the role of microorganisms in various industrial processes, including the production of biofuels, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. This type of research may also involve developing and testing new methods for improving the efficiency and sustainability of these processes.
Overall, microbiology laboratories play a critical role in advancing our understanding of microorganisms and their role in various biological, ecological, and industrial systems. The research that is carried out in these facilities has the potential to inform the development of new diagnostic tests, treatments, and technologies, and to improve our understanding of the complex interactions between microorganisms and the world around us.
Advantages of working in microbiology laboratories
1.The ability to make a positive impact on society: Microbiology research can lead to the development of new vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools that can help to improve public health and prevent the spread of diseases.
2.The opportunity to work with cutting-edge technology: Microbiology laboratories often have state-of-the-art equipment and technologies, such as high-tech microscopes, gene sequencing machines, and computer simulations, which can be both exciting and challenging to work with.
3.The chance to be at the forefront of scientific discovery: Microbiology is a rapidly advancing field, and working in a laboratory gives you the opportunity to be on the front lines of new discoveries and innovations.
4.The opportunity to work with a diverse team of scientists: Microbiology research is often conducted by teams of scientists with diverse backgrounds and expertise, which can make for a dynamic and collaborative work environment.
5.The potential for career advancement: Working in a microbiology laboratory can provide valuable experience and training that can lead to career advancement in academia, industry, or government.
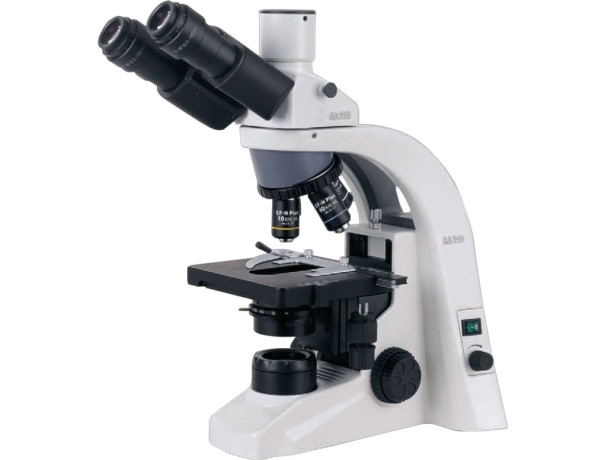
Equipment for Microbiology Laboratories
Microbiology laboratories are equipped with a wide range of specialized equipment and tools that are used to identify, cultivate, and study microorganisms. Some of the most common types of Laboratory equipment that may be found in a microbiology laboratory include:
Microscopes: These are used to view and analyze microorganisms at high magnification, and may include light microscopes, electron microscopes, and other specialized types of microscopes.
Laboratory Incubators: These are used to cultivate and grow microorganisms under controlled conditions, and may include incubators that are designed for specific types of microorganisms or for particular applications.
Laboratory Centrifuges: These are used to separate and purify microorganisms or other biological materials by spinning them at high speeds.
Pipettes and micropipettes: These are used to measure and transfer small volumes of liquids, and may be used for a variety of purposes, including the preparation of media and solutions, and the performance of assays and experiments.
Autoclaves: These are specialized pressure chambers that are used to sterilize equipment and materials by exposing them to high temperature and pressure.
Biosafety cabinets: These are specialized enclosures that are used to handle and manipulate potentially hazardous microorganisms in a safe and controlled manner.
Microbial identification systems: These are specialized systems that are used to identify microorganisms based on their characteristics and properties, and may include methods such as microscopy, culture-based methods, and molecular methods.
Molecular biology equipment: This may include equipment such as PCR machines, sequencers, and other specialized instruments that are used to study the genetics and metabolism of microorganisms.
Overall, the specific equipment that is used in a microbiology laboratory will depend on the specific focus and mission of the laboratory, as well as the needs of the researchers and clinicians who are using the facility.
Centrifuges for Microbiology Laboratory
choosing the right centrifuge involves a careful consideration of features. Speed and capacity must align with the nature of the experiments, and safety features ensure a secure working environment. Programmability adds a layer of convenience, allowing researchers to tailor centrifugation parameters to their specific needs.
Centrifugation Techniques in Microbiology
Centrifugation techniques are the unsung heroes behind many breakthroughs in microbiology. From sedimentation to density gradient centrifugation, these methods pave the way for isolating and studying cellular components with precision.
Role of Centrifuges in Microbial Research
Centrifuges play pivotal roles in DNA and RNA extraction, enabling the unraveling of genetic mysteries. Moreover, these powerful devices aid in protein purification and analysis, contributing to our understanding of microbial structures and functions.
Microscopes for microbiology laboratory
Microscopes are essential tools in microbiology laboratories, allowing scientists and researchers to study microscopic organisms and structures. There are different types of microscopes suitable for various microbiological applications