Laboratories are essential places where scientific research, experiments, and analyses take place. To conduct these activities efficiently, a wide range of laboratory apparatus is required. These apparatuses help scientists, researchers, and students carry out experiments, measurements, and observations accurately and safely. In this article, we will explore various types of laboratory apparatus and their functions, providing insights into the crucial role they play in scientific investigations.
Laboratory apparatus refers to a diverse array of tools and equipment used in scientific settings to conduct experiments, collect data, and analyze results. These instruments aid in performing precise and reliable experiments, which are fundamental to the advancement of various scientific fields.
Laboratory Equipment
Here are recommended Laboratory Equipment
Glassware
Glassware is an indispensable part of any laboratory. It includes items like beakers, test tubes, Erlenmeyer flasks, and graduated cylinders. These vessels are used to mix, heat, and store liquids and solutions during experiments.
Thermometers are vital for measuring temperature accurately. Different types of thermometers, such as mercury, digital, and infrared, cater to various temperature ranges and experimental requirements.

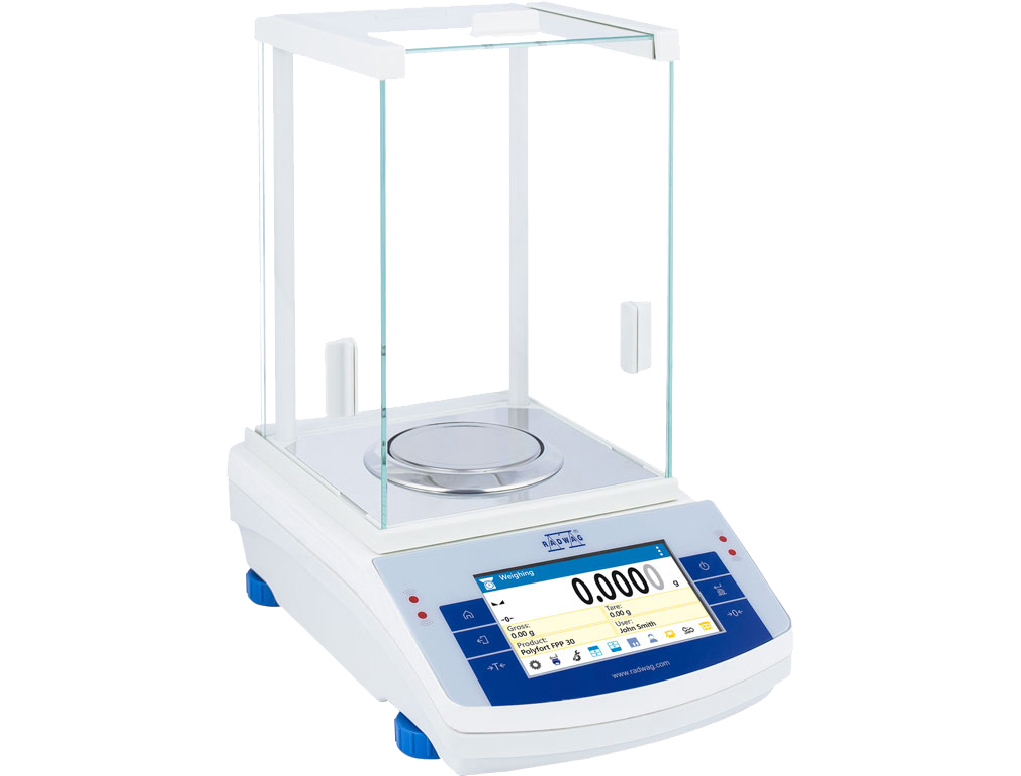
Laboratory Balances and weights are used to determine the mass of substances with high precision. They are essential in analytical chemistry, where small quantities matter significantly.

Lab Safety Equipment
Safety should be a top priority in laboratories. Safety equipment like fire extinguishers, first aid kits, and emergency showers must be readily available to respond quickly to accidents.
Lab Burners
Lab burners, such as Bunsen burners, provide controlled heat for experiments. They are vital in various chemical reactions and sterilization processes.
Measuring Instruments
Pipettes and Burettes
Pipettes and burettes are used to measure and transfer precise volumes of liquids. They are commonly employed in analytical chemistry and titration experiments.
Graduated Cylinders
Graduated cylinders are tall, narrow containers with calibrated markings used to measure liquids accurately.
Beakers
Beakers are versatile containers used for mixing, heating, and holding liquids during experiments.
Erlenmeyer Flasks
Erlenmeyer flasks have a conical shape with a narrow neck, ideal for swirling liquids and preventing spills during stirring.
Test Tubes
Test tubes are small cylindrical containers used to hold small quantities of substances during reactions or observations.
Heating and Cooling Equipment
Hot Plates
Laboratory Hot plates provide a flat heated surface for heating substances in glassware. They offer precise temperature control and are commonly used in chemistry and biology laboratories.

Bunsen Burners
Bunsen burners are gas burners that produce an adjustable flame for heating, sterilizing, and combustion purposes.
Heating Mantles
Heating mantles are electrical devices that wrap around glassware, providing even and controlled heating for delicate substances.
Refrigerators and Freezers
Refrigerators and freezers are essential for storing temperature-sensitive samples and reagents.
Analytical Instruments
Spectrophotometers are used to measure the intensity of light absorbed by a sample. They are instrumental in various applications, including quantitative analysis and DNA testing.
Gas Chromatographs
Gas chromatographs separate and analyze volatile compounds in a sample, making them indispensable in analytical chemistry and forensic investigations.
pH Meters
pH meters measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, crucial for maintaining optimal conditions in chemical reactions and biological processes.
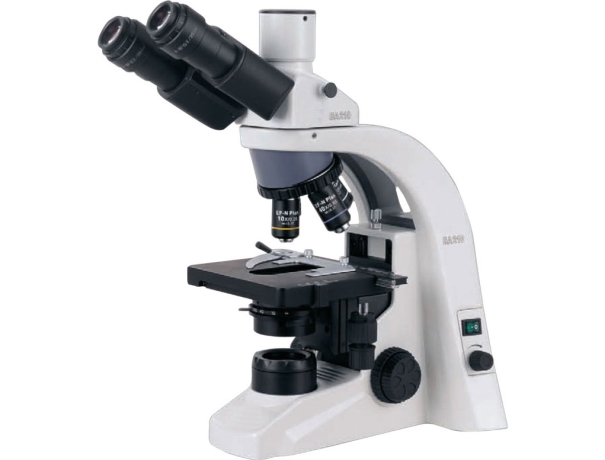
Microscopes enable scientists to observe and study microscopic organisms, cells, and structures, opening up a new world of discoveries in biology and medicine.
Centrifuges
Centrifuges spin samples at high speeds, separating components based on their density. They are used in biochemistry, medicine, and environmental research.
Separation Techniques
Filtration Apparatus
Filtration apparatus separates solids from liquids by passing the mixture through a porous material called a filter.
Distillation Setups
Distillation setups are used to separate components in a liquid mixture based on their boiling points.
Chromatography Columns
Chromatography columns separate and analyze mixtures based on their differential affinity for a stationary phase.
Safety and Protective Gear
Safety Goggles
Safety goggles protect the eyes from chemical splashes, fumes, and flying particles during experiments.
Lab Coats and Aprons
Lab coats and aprons shield the body and clothing from spills and potential hazardous materials.
Gloves
Gloves provide hand protection when handling chemicals, biological samples, and other hazardous substances.
Face Shields
Face shields offer additional protection for the face, particularly in experiments involving potential splashes or aerosols.
Specialized Laboratory Apparatus
Laboratory Incubators
Laboratory Incubators provide controlled and stable conditions for cell culture and microbial growth.
Autoclaves
Autoclaves use steam and pressure to sterilize equipment and laboratory waste, preventing contamination.
Fume Hoods
Fume hoods help to contain and exhaust harmful fumes and vapors generated during experiments.
Laboratory Water Baths
Water baths maintain a constant temperature for incubation, heating, and thawing processes.
Shakers and Stirrers
Shakers and stirrers are used for mixing and agitating samples in containers.