MRC offers a wide and professional range of Laboratory Glove Boxes for research and processing of air-sensitive materials and components under inert atmosphere . MRC also supply customized system solutions for thermal treatment, vacuum coating, operator safety and more. All MRC Glove box Systems are manufactured using the strictest of Quality Assurance measures and with only the highest quality components including Swagelok compression fittings and valves, Edwards Vacuum Components and Allen Bradley PLC Controls.
What are Laboratory Glove Boxes
Glove boxes are Isolated chamber with arm ports or gloves. arm ports are arranged in such a way that the user can place their hands into the gloves and perform tasks inside the box without breaking containment.

Applications of Laboratory Glove Boxes
MRC glove box applications are:
-Personal Protection from hazardous substances
-Battery research
-Organic Electronics Organic light emitting diodes (devices)
-Additive Manufacturing
-Welding process in a controlled environment.
- Material Purification
- Thermal Treatment
- Perovskite materials research - solar cells
-Chemistry
-Stem Cell Research
-Microbiology
-Clostridium difficile
-Cancer Cell research
-Anaerobic research
-Life Science
-Clinical
-Coronavirus
-Pharmaceutical research
-Infectious Diseases
-Animal Research
-General Lab Studies
The Comprehensive Applications of Laboratory Glove Boxes
Glove boxes are vital for a broad spectrum of applications across industries, from battery research to pharmaceuticals, welding to nuclear science, and organic electronics to nanotechnology. These enclosures protect both the sensitive materials inside and the researchers handling them, making them indispensable tools in modern scientific and industrial operations. As new technologies emerge, glove boxes will continue to evolve, providing safe and controlled environments for the cutting-edge work of tomorrow.
They are highly specialized enclosures designed to allow users to manipulate objects in a controlled atmosphere while remaining physically separated from the internal environment. They are crucial in a wide range of scientific, industrial, and medical applications where sensitivity to air, moisture, and contamination is paramount.
1. Inert Atmosphere Work
One of the most common applications is in environments that require a strict control of oxygen and moisture levels. These enclosures are filled with inert gases like nitrogen, argon, or helium to create a protective atmosphere. This type is often used in:
Semiconductor Manufacturing: The production of semiconductor devices requires contamination-free environments, especially when handling materials like silicon wafers and sensitive coatings.
OLED and Thin-Film Research: Organic light-emitting diodes and thin-film photovoltaics are highly sensitive to oxygen and moisture, and glove boxes ensure stable production conditions.
Catalyst Research: Many catalysts degrade or react when exposed to oxygen or moisture, making glove boxes essential for their preparation and storage.
2. Battery Development and Research
The rise of lithium-ion and other advanced battery technologies has greatly increased the demand for glove boxes in research and production. Batteries often contain reactive materials such as lithium metal, which can ignite when exposed to air or water vapor.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: In battery research, particularly for electric vehicles and energy storage, They are used to assemble battery cells in a dry and oxygen-free environment. This prevents undesirable reactions that could compromise cell integrity or lead to dangerous outcomes like fires.
Solid-State Batteries: These batteries utilize solid electrolytes, which are highly sensitive to moisture. Glove boxes provide the necessary protection to ensure that these materials remain stable during assembly and testing.
3. Welding in Controlled Environments
Glove boxes are also utilized in specialized welding applications where metals or alloys must be protected from oxidation or contamination. Materials like titanium, aluminum, and certain stainless steels can react negatively with oxygen during welding, leading to poor joint quality and structural weaknesses.
Titanium Welding: Titanium is highly reactive with oxygen and requires an inert environment, often provided by a glove box filled with argon gas. The controlled atmosphere ensures clean, defect-free welds, particularly in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive.
4. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Containment
Glove boxes serve as essential containment systems for protecting personnel from hazardous substances while allowing safe manipulation of dangerous materials.
Radiation Safety: In nuclear research and radioisotope handling, glove boxes provide a critical barrier between the user and radioactive materials, minimizing the risk of exposure.
Hazardous Chemicals and Biological Agents: In biochemistry and virology laboratories, They are used to handle dangerous pathogens, toxic chemicals, and other hazardous substances that require containment to ensure operator safety.
5. Pharmaceutical and Biotech Applications
In the pharmaceutical industry, glove boxes are important role in research and production, especially when handling highly sensitive biological samples or volatile chemicals.
Aseptic Processing: Glove boxes allow for the handling of drugs, especially injectable medications, in a sterile environment, preventing contamination and ensuring that the final product meets safety and efficacy standards.
Biological Research: Biotechnologists use glove boxes to manipulate genetically modified organisms, culture cells, or handle hazardous biological samples. Glove boxes help maintain sterility and protect sensitive experiments from outside contaminants.
6. Organic Electronics
Organic electronics, such as organic photovoltaics (OPVs) and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), are materials that degrade quickly when exposed to oxygen and moisture. Glove boxes create ideal environments for processing and assembling these devices.
OLED Production: The fabrication of OLED displays and lighting solutions requires precise environmental controls to prevent material degradation during the manufacturing process.
Organic Photovoltaics: OPVs are used in flexible, lightweight solar cells. Glove boxes ensure that the materials remain in optimal condition for efficient energy conversion.
7. Perovskite-Based Solar Cells
Perovskite solar cells are a rapidly developing technology with significant potential for high-efficiency energy generation. However, perovskite materials are extremely sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring careful handling within glove boxes.
Material Synthesis and Device Fabrication: Researchers use glove boxes to synthesize perovskite materials and fabricate solar cells in a moisture-free environment. This ensures that the cells perform optimally and have a longer operational lifespan.
8. Material Science and Nanotechnology
They are invaluable in the field of materials science, particularly when working with air-sensitive compounds, reactive metals, and nanomaterials.
Nanomaterial Synthesis: Nanoparticles, quantum dots, and nanowires are often sensitive to air and moisture, necessitating the use of glove boxes during their production and handling.
Air-Sensitive Metals and Alloys: Certain metals, such as rare earths and alkali metals, oxidize rapidly when exposed to air. Glove boxes provide an inert environment to work with these materials safely.
9. Nuclear and Radioactive Material Handling
In nuclear research and industry, glove boxes provide a crucial protective barrier between researchers and radioactive materials.
Radiochemistry: Handling radioactive isotopes in a controlled environment ensures that researchers can safely conduct experiments without the risk of contamination.
Nuclear Fuel Processing:used to handle and process nuclear fuel and waste, keeping radioactive materials safely contained while allowing for precise manipulation.
10. 3D Printing with Reactive Metals
Glove boxes are increasingly being integrated into 3D printing systems that use reactive metals, such as titanium, aluminum, and magnesium.
Additive Manufacturing: In industries like aerospace and healthcare, glove boxes provide a controlled atmosphere for 3D printing with metals that oxidize or degrade in the presence of oxygen or moisture, ensuring high-quality and defect-free prints.
Types of glove boxes
-With gas purification system(for chemistry,batteries,Oleds, Perovskite)

-Inert gas,Argon or Nitrogen. (for chemistry,batteries,Oleds, Perovskite)
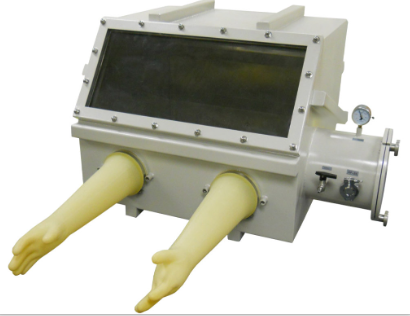
-Vacuum glove box
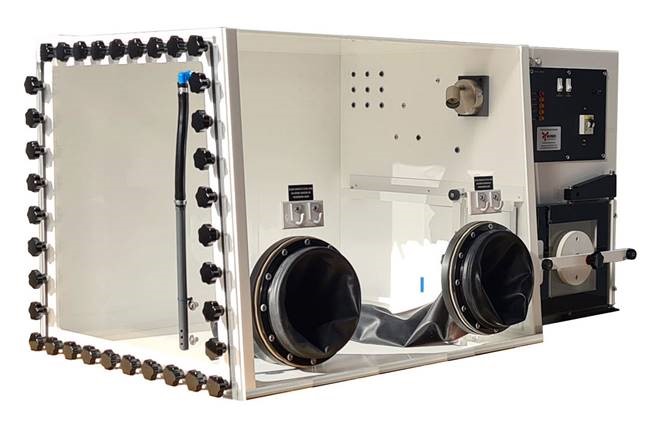

-Anaerobic glove box

-Laboratory Acrylic Glove Boxes

Uses of laboratory glove boxes:
Here are some key functions and uses of laboratory glove boxes:
Protection from Hazardous Materials: Glove boxes prevent exposure to toxic, radioactive, or biohazardous substances by creating a physical barrier between the user and the material.
Inert Atmosphere: Some glove boxes maintain an inert gas atmosphere (such as nitrogen or argon) to prevent reactions with oxygen, moisture, or other contaminants, which is useful in chemical and materials science experiments.
Sterile Environment: Used in biological research or pharmaceutical manufacturing to maintain a sterile environment for sensitive processes.
Vacuum or Controlled Pressure: Certain types of glove boxes allow work under vacuum or controlled pressure conditions.
Handling of Radioactive Materials: In nuclear laboratories, glove boxes are used for manipulating radioactive materials safely.
What are Vacuum Glove Boxes for the laboratory?
A vacuum glove box is a sealed container designed for handling sensitive materials in a controlled environment. It allows researchers to perform tasks while protecting the samples from air, moisture, or other environmental contaminants, which is critical for experiments involving highly reactive or toxic materials.
Here are some key features and uses:
Structure:
Sealed Chamber: The main compartment of the glove box is airtight, ensuring the inside atmosphere can be controlled and maintained.
Gloves: Integrated gloves extend into the box, allowing users to manipulate objects inside without breaking the sealed environment.
Vacuum Capability: A vacuum system is used to remove air or replace it with inert gases like nitrogen or argon, creating an atmosphere free from oxygen or moisture.
Applications:
Chemistry and Material Science: To handle air-sensitive chemicals like alkali metals or compounds that degrade in the presence of oxygen or water.
Electronics and Semiconductor Research: For creating or testing components in a contamination-free environment.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology: Protecting sensitive biological samples from contamination.
Best Laboratory Glove Boxes
MRC offers a wide and professional range of Laboratory Glove Boxes