MRC introduces professional MICROSCOPES and MICROSCOPES accessories for labs and industry.
A microscope is an instrument that can be used to observe small objects, even cells.
The main differences between the different microscopes are mainly in the magnification level of the microscope and the quality of the image obtained.
Types of microscopes
In general, microscopes are divided into two types: high power and low power.
A high-power microscope is used to look at very tiny things like bacteria, blood cells, cell nuclei, etc.
A low-power microscope is designed to look at larger objects, such as electronic cards, fly wings, fabric weaves, coins, stamps, sand grains and more.
The microscopes have a different shape according to the number of eyepieces available at the top of the device: monocular, binocular and trinocular.
Low-power microscopes = stereo microscopes, surgical microscopes.
High power microscopes = complex microscopes, biological microscopes.
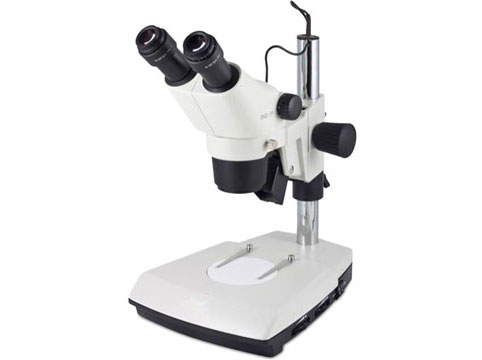
Stereo microscopes-The Stereo microscope has two optical paths at slightly different angles allowing the image to be viewed three-dimensionally under the lenses.
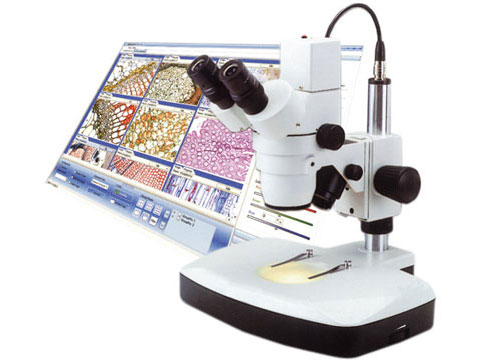
Digital microscopes-uses the power of the computer to view objects not visible to the naked eye.The advantage of a digital microscope is that you can email the images and save them on your computer.
Key features of digital microscopes include:
Digital Imaging: Images or videos are captured digitally, making it easier to save, analyze, and share data.
Magnification Range: They offer a wide range of magnification, often adjustable through software, from low to very high levels, depending on the model.
Ease of Use: With no eyepieces to look through, digital microscopes are more comfortable for prolonged use.
Software Integration: These microscopes often come with software for measuring, annotating, and enhancing images, making them suitable for educational, industrial, and scientific purposes.
Connectivity: They can be connected to computers or other devices via USB or wireless connections, making them portable and easy to integrate into digital workflows.
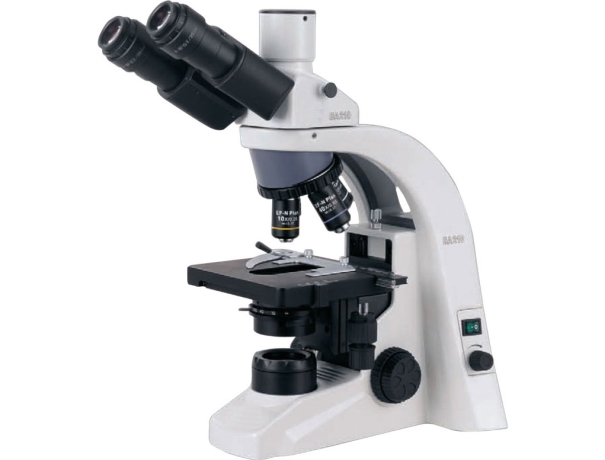
Biological microscopes-A biological microscope is a type of optical microscope used to observe cells, tissues, and other biological specimens.
Key features of biological microscopes include:
Compound Lens System: Biological microscopes usually have multiple lenses (objective and eyepiece lenses) to achieve high magnification, typically ranging from 40x to 1000x or more.
Light Source: They use a built-in light source, often below the stage, to illuminate transparent or semi-transparent specimens, which helps in clear viewing of the samples.
Objective Lenses: These microscopes have several interchangeable objective lenses (such as 4x, 10x, 40x, 100x) to vary the magnification levels for detailed study.
Stage and Slides: Specimens are placed on glass slides and viewed on the microscope’s stage. The stage often includes mechanical controls to move the slide precisely.
Uses: They are used for studying biological structures like cells, bacteria, algae, fungi, and tissues, making them essential in fields like biology, medicine, and microbiology.
Staining Techniques: Often, biological samples are stained with dyes to enhance contrast and make specific structures more visible under the microscope.